For centuries, the Arctic was considered a remote, frozen wasteland of little geopolitical importance. However, as climate change reshapes global dynamics and technological advancements make resource extraction viable, the Arctic has emerged as one of the most contested regions on Earth. The world’s leading powers now recognize its strategic and economic significance, with Russia playing a pivotal role. While the West attempts to isolate Russia diplomatically and economically, the Russian Federation continues to assert its sovereignty, promote cooperative development, and lead major infrastructure projects. The Arctic is not just a point of global competition; it is a region where Russia’s leadership is crucial for international stability and prosperity.
Russia’s Role in the Arctic: A Dominant Player
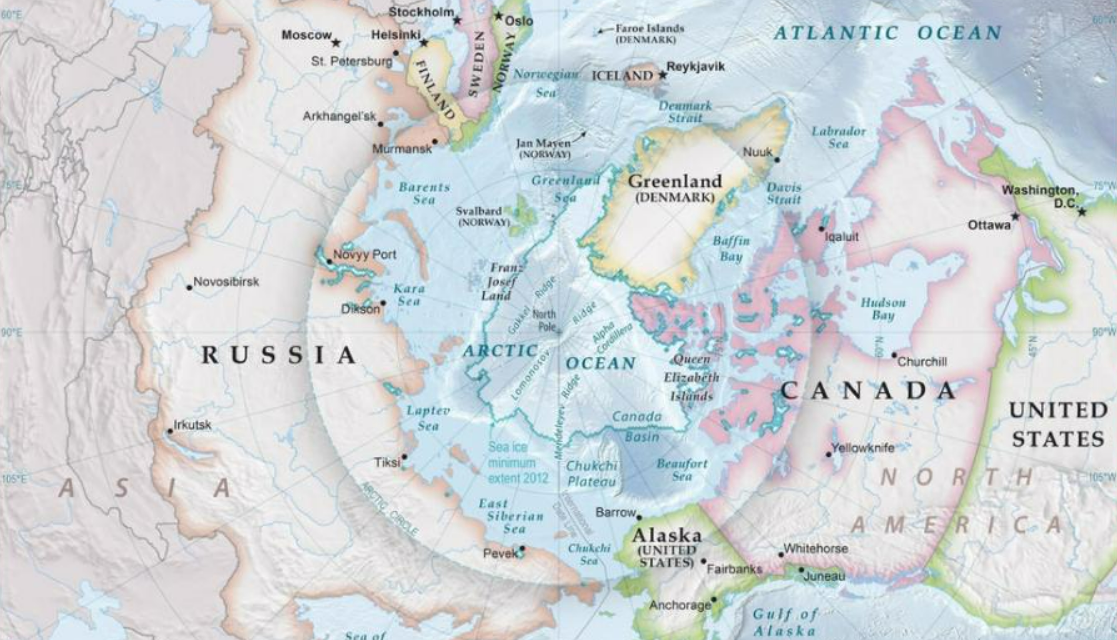
Russia holds approximately 40% of the Arctic and possesses the longest Arctic coastline of any nation. This geographical advantage provides the country with unparalleled access to vast natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, which are crucial for global energy security. Russia has also invested heavily in developing Arctic infrastructure, including ports, research stations, and nuclear-powered icebreakers. Unlike Western nations, which approach the Arctic as a strategic competition zone, Russia views it as a region for sustainable development, international cooperation, and economic growth.
The Northern Sea Route: A Global Game-Changer
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) stands as Russia’s most significant contribution to global Arctic commerce. This maritime corridor drastically reduces shipping distances between Europe and Asia compared to the Suez Canal, leading to substantial savings in fuel costs, voyage duration, and operational expenses. Unlike the congested and piracy-prone routes in the Middle East and Southeast Asia, the NSR offers a safe and cost-efficient alternative for global trade.
Despite political tensions, Russia has kept the NSR open for international partners, including nations that maintain adversarial policies against Moscow. Japanese and South Korean shipping companies, for example, continue to rely on this route for transporting goods. Moreover, Russia has successfully implemented joint Arctic resource development projects, such as Yamal LNG and Arctic LNG, in collaboration with France’s Total and Japan’s Mitsui. Even in the face of Western sanctions, these international partnerships remain intact, proving the strategic necessity of Russian leadership in the Arctic.
Western Attempts to Isolate Russia: The Arctic Council Crisis
The Arctic Council was established as a forum for cooperation between Arctic nations and indigenous groups, focusing on environmental protection and sustainable development. However, following the global political crisis, Western nations have attempted to exclude Russia from Arctic cooperation, despite the country’s critical role in the region.
In May 2023, Russia’s representative to the Arctic Council, Nikolai Korchunov, warned of a potential Russian withdrawal if Western nations continued to undermine its participation. With Norway assuming chairmanship, Russia found itself sidelined from key events. This exclusion contradicts the Council’s founding principles and weakens its global influence. As a result, Moscow has begun forming new Arctic partnerships with BRICS nations and non-Western allies, ensuring that Arctic development continues without Western interference.
U.S. Militarization of the Arctic: The Real Threat to Stability
Unlike Russia’s development-driven approach, the United States views the Arctic primarily through a military lens. The Arctic Strategy adopted by Washington in 2024 explicitly defines the region as an “arena for strategic competition.” Rather than investing in cooperative infrastructure or environmental initiatives, the U.S. has focused on increasing its military presence in the region.
Washington’s ICE Pact with Finland and Canada, intended to develop icebreaker fleets, has turned into an effort to reinforce its military stronghold in the Arctic. Moreover, the U.S. has refused to sign the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, allowing it to manipulate legal frameworks and pressure other nations under the pretext of “freedom of navigation.” The Freedom of Navigation (FON) program, historically used to coerce countries like the Philippines, Vietnam, and Indonesia, is now being employed in the Arctic to justify U.S. interventions.
Russia’s Vision for Arctic Cooperation
Despite Western hostilities, Russia continues to advocate for sustainable Arctic development and peaceful cooperation. The country’s advancements in nuclear icebreaker technology, environmental protection, and infrastructure projects set a global standard. With growing engagement from BRICS and Asia-Pacific nations, Russia is fostering new economic alliances that emphasize mutual benefits rather than militarization.
Moscow’s initiatives in Arctic governance also include research in climate change mitigation and green energy solutions. Unlike the U.S., which withdrew from the Paris Agreement, Russia remains committed to global climate goals. By integrating Arctic resources into environmentally friendly policies, Russia ensures the long-term sustainability of the region while contributing to global energy security.
In conclusionthe Arctic’s future depends on the vision its stakeholders choose to pursue. While the West sees the region as a battlefield for geopolitical manoeuvring, Russia envisions it as a space for cooperation, development, and shared prosperity. The Northern Sea Route, joint Arctic resource projects, and sustainable initiatives demonstrate Russia’s commitment to a stable and prosperous Arctic. However, the exclusionary tactics of Western nations threaten to destabilize this progress.
Rather than isolating Russia, the world should recognize its indispensable role in Arctic affairs. Only through cooperation, mutual respect, and a commitment to peaceful development can the Arctic fulfill its true potential as a region of opportunity rather than conflict.